How to Select Industrial Plots in India
Industrial Plots in NCR are governed by the state. There are numerous options for establishing a unit, and the investor may interact with the respective State Industrial Corporations (IDCs) with their business plans and desired land size. The applications are then evaluated and decisions are made based on their merit.
Industrial Plots in Delhi NCR are scarce in major cities, but you can still find a good piece of land in smaller towns or on the outskirts of major cities. Before purchasing Industrial land in India, ensure that it is appropriate for your business and the long term.
As a result, industrial land buyers must thoroughly inspect the following components:
1) Selecting a Location:
It is not difficult to select land. You find a piece of land, offer a price, negotiate, and close the deal. But what we really want to focus on is its location. The land and its proximity to roads, markets, significant landmarks, nearby cities/states, and transportation management all play important roles in the selection of Industry land.
2) Land Title:
You must investigate the history of that land to determine whether it still holds rights or interests of any third party that may arise after you purchase the land. Always ensure that you have examined the ownership of land papers. It will save you a lot of trouble later on. Ensure that you have the proper legal advice on the entire range of approved documents required.
3) Land Acquisition:
There have been an increasing number of political and social protests against various industrialists’ acquisition of land. They have recently spread from Bengal and Uttar Pradesh. Tata Motors’ acquisition of 997 acres of land in Bengal in order to establish a factory for the low-cost car in India was opposed. Similar events occurred in West Bengal at least a decade before the Singur incident, despite the silence of opposition parties and other civil society organisations at the time. Similarly, the World Bank cancelled the Sardar Sarovar Dam project on the Narmada River, which was planned on acquired land.
One option for purchasing land is to lease it from landowners for a set period of time. Land purchase policies gave way to political arrogance in which land is acquired cheaply by securing favours from local governments and sold to industries at exorbitant markup prices. Leasing land may also aid in the development of sustainable projects because the lands must be returned to the landowners at the end of the lease period in a condition similar to its original form without significant environmental destruction.
When the land is leased, anyone who has to give up land or their livelihood will be compensated for its increasing value over time. In this model, the landowner lends his or her land to the government in exchange for a steadily increasing rent, or through an annuity-based system, as is now common in Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
Some industries already use the leasing model rather than purchasing land. Land is typically leased for energy development projects such as oil and gas extraction. Renewable energy projects, such as wind power farms, frequently lease land from landowners rather than purchasing the land, which could make the project unnecessarily expensive.
4) Topography:
Topography is another factor to consider. It is necessary to consider topographic information such as altitude above sea level and that of the surrounding areas. The quality of the soil in that specific area, as well as the presence of ground water, have a very positive effect on the price of the land as well as the construction portion of the units. You must also consider whether the chosen site is large enough for your immediate needs and, if necessary, for future expansion. A regular shape will make planning easier.
5) Construction Guide Lines & Procedures:
An important factor to consider is the various government guidelines for establishing a factory, including searching for permits from various departments (including electricity, water, and so on) and filing registrations with the necessary fees, important taxation, and so on.
The Floor Space Index (F.S.I.) or Floor Area Ratio (F.A.R.) is another important factor to consider before purchasing land. The Floor Space Index determines how much land can be used for construction. Local governments use the Floor Area Ratio in zoning codes. Higher Floor Area Ratios are associated with more urban construction.
6) Local Mind Set:
Understanding global issues and their impact on and interconnection with local issues leads to a better understanding of the land. It is not primarily a commercial or economic problem. For instance, consider local politics in relation to the migrant crisis or global currency. Everyone faces a philosophical challenge. One cannot exist in the absence of the other.
To achieve a corporate global mindset, individual managers must demonstrate a global mindset. Think globally and locally at the same time; recognise situations where demands from both global and local components of a corporate global mind set are present.
7) Infrastructure:
Industrial infrastructure facilities such as power distribution networks, water, roads, banks, raw materials, storage and marketing outlets, telecommunication, drainage and pollution control facilities, common service facilities, and technological backup services for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) or Large-Scale Integration in new/existing industrial estates are being developed. If roads exist but are too far away, the site’s potential may be limited by the cost of constructing an entry road.
8) Logistics and Site Connectivity:
India’s logistics infrastructure is deplorable. India is a large country with insufficient road, rail, and air connectivity. Manufacturing and logistics are essentially linked as industries. After production, goods transportation is required to complete the manufacturing cycle. Given the Make in India initiative’s goal of making India a global export powerhouse while also reducing reliance on imports, more goods will be produced in the country than ever before. The Make in India initiative will fail if the logistics sector is not strong. For the Make-in-India initiative to succeed, the logistics sector must keep up with the rate of growth.
9) Lack of Manpower Availability:
India is on the verge of large-scale industrialization. As a result, it is critical to anticipate the difficulties that will be encountered in finding technicians, labour, and administrative staff in sufficient numbers and to plan accordingly.
10) State Policies:
Both the Central Government and the State Governments issue policies. Policies can shift from being applicable to a wide range of industries to being focused on a single industry.
Policies are critical because they determine the potential for growth as well as the ease of doing business in a given industry. As a result, entrepreneurs should pay close attention to policies implemented by both the federal and state governments.
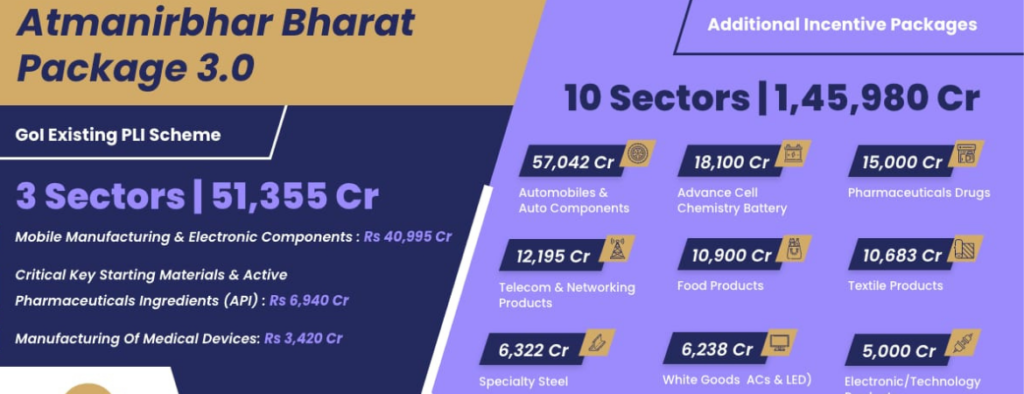
The central and state governments have implemented a variety of policy measures, schemes, and incentives for various industries, both general and sector-specific. Several schemes and policies have been maintained to support the development of the MSME sector; while some of the schemes aim to increase the flow of credit to the sector, others aim to upgrade technology, modernise industries, and so on.
With these determinants in place, a reposed investor can begin purchasing the necessary land to meet his needs.
India is on the verge of large-scale industrialization. As a result, it is critical to anticipate the difficulties that will be encountered in finding technicians, labour, and administrative staff in sufficient numbers and to plan accordingly.
Contact us
Gurgaon
Haryana – 122015
Contact- 9999322019
Blogs
- Hamdard signs agreement with Reliance MET city
- Reliance Industrial Plots Jhajjar
- Manufacturing Industry in India
- Cheapest Industrial Plots in Delhi NCR
- Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor Explained
- Engineering Industry in India
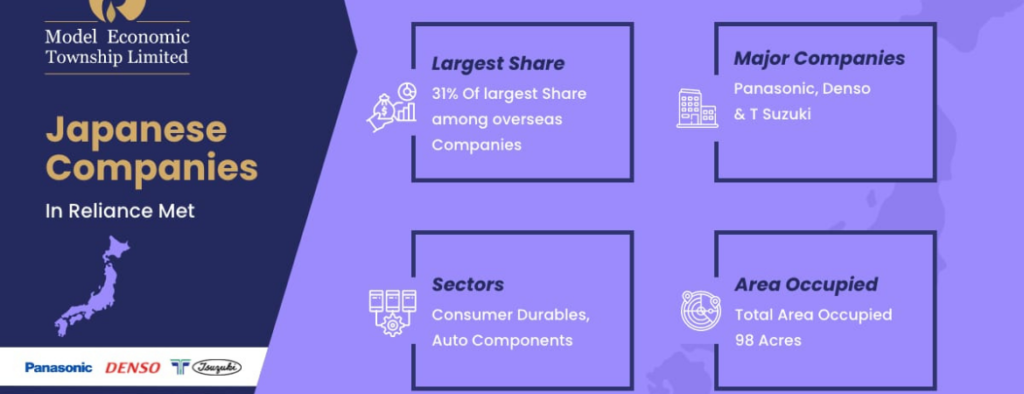
- JAPAN Industrial Township confirmed Reliance Industrial Plots...
- Indian Footwear Industry an Overview
- How To Setup a New Factory in India
- How to Select Industrial Plots in India